Mezzanine flooring is a fascinating aspect of architectural design and construction, offering versatile solutions to optimize space utilization in various settings. Here’s an in-depth exploration of all things related to mezzanine flooring, its uses, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Mezzanine Flooring
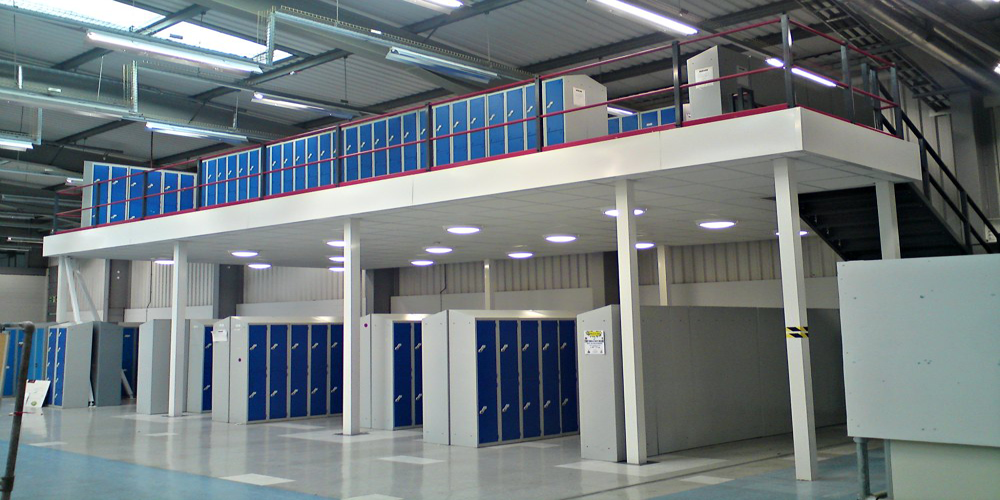
Mezzanine flooring refers to an intermediate floor within a building, typically between the main floors, which doesn’t encompass the entire floor space. It’s a raised platform that often overlooks the lower level, creating additional functional space without expanding the building’s footprint. Mezzanine floors are known for their adaptability and can be found across diverse sectors, including commercial, industrial, and residential spaces.
Uses and Applications
Commercial Spaces
Warehouses and Distribution Centers: Mezzanine floors in warehouses optimize vertical space, allowing for increased storage capacity without the need for a larger facility.
Retail Stores: Retailers often utilize mezzanine floors to expand display areas, create offices, or add more stock storage.
Office Buildings: Mezzanine levels in offices accommodate meeting rooms, breakout areas, or additional workspace.
Industrial Settings
Manufacturing Plants: Mezzanines provide space for machinery, assembly lines, or storage of raw materials, optimizing production workflows.
Logistics Centers: Efficient storage of goods and inventory management are facilitated by mezzanine floors in logistics facilities.
Residential Spaces
Loft Apartments: Mezzanine floors in residential spaces often serve as bedrooms, studies, or lounges, maximizing vertical living space.
Home Offices: Utilized for remote workspaces or hobby areas without altering the main living areas.
Advantages of Mezzanine Flooring
Space Utilization
Mezzanine floors optimize unused vertical space, effectively doubling the available area without the need for additional land or extensive construction.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to building extensions or moving to larger premises, installing a mezzanine floor is often a more cost-effective solution.
Customization and Flexibility
Mezzanine floors can be customized to suit specific requirements, allowing for flexibility in design, usage, and layout.
Quick Installation
The construction of mezzanine floors is generally quicker than traditional building extensions, causing minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
Increase Property Value
Adding a mezzanine floor can potentially increase the property’s value by enhancing its functionality and usable space.
Types of Mezzanine Flooring
Structural
Free-Standing: These mezzanines are self-supporting and do not rely on the building’s structure for support.
Rack-Supported: Utilizes existing pallet racking as a structural support for the mezzanine.
Steel I-Beam: Constructed using steel I-beams as primary support, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Accessory Elements
Stairs and Ladders: Various types of access points including stairs, ladders, or even elevators for larger mezzanines.
Handrails and Guardrails: Essential safety features to prevent falls and ensure compliance with regulations.
Considerations before Installation
Building Regulations
Permits and Approvals: Ensure compliance with local building codes and obtain necessary permits before installation.
Safety Standards: Adhere to safety regulations for load-bearing capacity, fire safety, and accessibility.
Structural Integrity
Building Assessment: Assess the building’s structural integrity to support the additional load of the mezzanine floor.
Functionality and Design
Purpose and Usage: Determine the intended function of the mezzanine to plan its design and layout effectively.
Aesthetics: Consider design elements that align with the overall aesthetics of the space.
Mezzanine Flooring a Practical Solution
Mezzanine flooring offers a practical solution to maximize space utilization across various sectors. Its adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility make it a popular choice for businesses and homeowners seeking to optimize space without extensive construction. Understanding its uses, advantages, types, and considerations before installation is crucial in harnessing its full potential while ensuring safety and compliance with regulations.